Learn how to spot and cease on a regular basis cyberattacks
Abstract created by Sensible Solutions AI
In abstract:
- PCWorld covers rising cybersecurity threats together with AI-powered ransomware, deepfake scams, malicious browser extensions focusing on crypto wallets, and vulnerabilities in sensible units and printers.
- These assaults matter as a result of they exploit on a regular basis digital actions, with attackers utilizing subtle strategies like faux captchas and compromised unsubscribe buttons to steal knowledge.
- Key defenses embrace avoiding suspicious unsubscribe hyperlinks, updating firmware recurrently, checking app permissions rigorously, and by no means pasting code into Home windows Run dialog when prompted by captchas. Detailed directions are supplied beneath.
From sensible however insecure door locks to Nvidia’s deepfake keynote, there are presently quite a few types of assault which can be extraordinarily harmful.
The next 9 assaults stand out specifically and will additionally pose a menace in an identical type in 2026.
1. Malware in open supply is on the rise
In 2024, the pc world narrowly escaped catastrophe: Over a number of years, attackers had been working to construct a backdoor into the Linux working system. A vulnerability on this system impacts nearly all customers, as nearly each web server runs on Linux.
The attackers had been on the verge of gaining undetected entry to a big proportion of those servers. They’d infiltrated the open supply undertaking XZ, which produces a compression device, by posing as staff. They achieved this by way of social engineering and an excessive amount of endurance.
The assault on the open-source software program presumably started in 2021 and continued till early 2024. By that point, the backdoor had penetrated pre-release variations of Debian and different Linux methods. It was then solely months away from being distributed to most web servers worldwide.
The backdoor was not found by an antivirus specialist, however by Andres Freund, a Microsoft worker. Freund is a developer and works on the open-source database PostgreSQL on Linux.
He observed that logging in through SSH (Safe Shell) took a bit longer with the brand new pre-release model of Debian. As a substitute of the same old quarter of a second, the login took three-quarters of a second.
Different builders may not have observed this distinction or might need ignored it. Nonetheless, Freund turned suspicious and looked for the trigger. 4 days later, he had discovered the backdoor and warned the general public.
Safety researchers then assigned the XZ backdoor a CVSS (Frequent Vulnerability Scoring System) rating of 10, the best doable worth.
SSH is used to attach a PC to a Linux server. Keys are exchanged for safety functions. In 2024, a backdoor that may very well be exploited through SSH nearly discovered its approach into Linux servers.
Foundry
The assault on XZ is particular for a number of causes. On the one hand, there’s the length. The attacker took years to turn into a member of an open supply undertaking, acquire the belief of the undertaking supervisor, and combine his code.
The malicious code and your complete assault chain are additionally noteworthy. It consists of XZ Utils, Systemd, and SSH.
The identical backdoor solely opens for the attacker, who should ship a secret key. All different SSH customers are denied entry to the backdoor. Lastly, the invention of the malicious code can also be extraordinary — simply in time and because of a single attentive developer.
It’s alarming that this extraordinary assault on an open-source undertaking is just not an remoted case. Though the opposite assaults are much less spectacular, they’re all of the extra quite a few.
That is doable as a result of open-source software program is predicated on openness: The code is accessible, customizable, and verifiable by anybody. Though there are safety mechanisms in place, it’s nonetheless comparatively simple to offer contaminated packages, that are then utilized by builders.
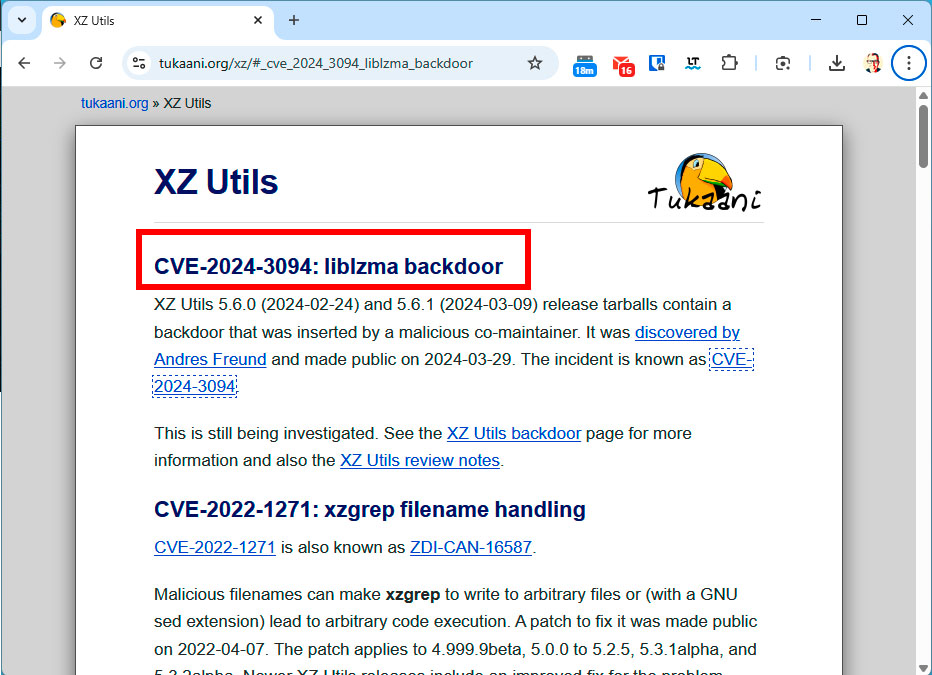
The safety vulnerability in XZ Utils has been given a rating of 10, which is the best doable worth. This reveals that the vulnerability might be simply exploited and trigger vital injury.
Foundry
Antivirus producer Kaspersky additionally attracts consideration to this. In accordance with an evaluation, cybercriminals hid a complete of 14,000 malicious packages in open-source initiatives in 2024. This represents a rise of fifty p.c in comparison with the earlier 12 months.
The consultants on the cybersecurity supplier examined 42 million variations of open-source initiatives for vulnerabilities. We don’t but have any figures for 2025. Nonetheless, we don’t count on a major decline.
Hazard: The danger to finish customers is extra oblique. Most assaults are aimed toward stealing knowledge from firms. Accordingly, it’s primarily enterprise software program that’s affected. Nonetheless, knowledge theft from firms finally additionally impacts clients.
Safety: For builders who combine open supply into their initiatives, in addition to for firms that work with open supply, safety supplier Kaspersky gives an data feed on problematic code.
The feed stories the next kinds of threats: packages with vulnerabilities, packages with malicious code, packages with riskware equivalent to crypto miners, hacking instruments, and so forth., compromised packages containing political slogans.
Entry to the feed might be requested at kaspersky.com/open-source-feed.
Software program firms may entry instruments from safety consultants equivalent to Xygeni Safety. The corporate makes a speciality of defending the software program provide chain. Finish customers should depend on their put in virus safety. See our article on the perfect antivirus packages.
2. Unsubscribe button steals knowledge
Each e-newsletter should comprise an unsubscribe button that means that you can unsubscribe.
Hazard: Not each unsubscribe hyperlink is innocent. One in 650 of those buttons doesn’t result in the specified unsubscribe web page, however to a phishing web site that desires to steal knowledge or unfold malware. That is reported by the safety firm DNS Filter.
Anybody who clicks on an unsubscribe hyperlink routinely confirms that their electronic mail deal with exists and that they verify their inbox. For spammers, who normally extract their electronic mail addresses from massive knowledge packages, this data alone is efficacious.
If the spammers go to the difficulty of designing the supposed unsubscribe web page in such a approach that it extracts knowledge from guests, they use social engineering methods to elicit passwords and different delicate data from their victims.
Safety: As a substitute of clicking on the unsubscribe button, you’ll be able to block the sender in your electronic mail program or within the net interface of your electronic mail supplier. If this isn’t doable, you’ll be able to add the e-mail and thus the sender to a spam listing.
This may stop any additional messages from this sender from reaching your inbox. You’ll then solely want to recollect to unblock the sender if you wish to obtain messages from them once more.
Nonetheless, it will by no means be the case with the phishing emails we’re discussing right here.
- In Outlook, right-click on an electronic mail and choose “Block” → “Block sender”.
- In Thunderbird, choose the e-mail and click on on “Junk” on the prime.
- In Gmail, open the message after which choose the three-dot menu on the prime proper of the e-mail. Within the menu, click on on “Report spam” or “Block sender”.
3. Captcha introduces malware
Captchas are designed to guard web sites from automated requests by distinguishing actual folks from bots. These days, this usually requires nothing greater than clicking on the “I’m not a robotic” checkbox.
Prior to now, you needed to click on on small picture squares displaying automobiles, site visitors lights, or bikes.
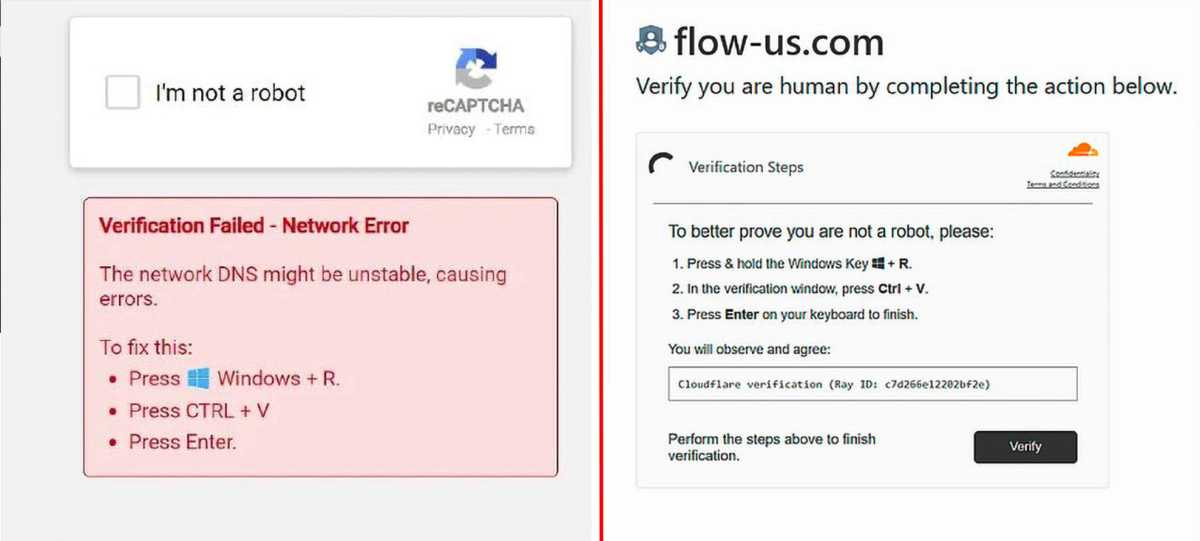
New lure with captchas: After clicking on the hostile captcha “I’m not a robotic”, considered one of these directions seems. For those who comply with it, you insert a beforehand copied malicious code into the Home windows Run dialog, which then downloads the precise virus.
Foundry
Hazard: For a while now, criminals have been utilizing captchas to smuggle viruses such because the Qakbot malware onto the PCs of web site guests, as follows:
- While you first click on on the “I’m not a robotic” checkbox, the web site copies malicious code to the web page customer’s clipboard.
- Directions then seem, which the consumer is meant to comply with as a result of a community error has allegedly occurred, or to proceed verifying that they’re a human and never a machine. The directions specify the important thing combos Win-R and Ctrl-V, adopted by the Enter key.
- Nonetheless, what this truly does is open the Home windows Run dialogue field (Win-R), paste the malicious code from the clipboard into it (Ctrl-V), and execute it (Enter).
- The code then downloads the precise malware, normally Qakbot. This provides the PC to a botnet or downloads ransomware that encrypts all knowledge after which calls for a ransom.
Safety: The Run dialogue field ought to function a transparent warning. No legit captcha on the earth ought to wish to paste code there. Stay suspicious and don’t be afraid to cancel an motion.
4. Spy ware Trojans within the App Retailer
A brand new sort of spyware and adware Trojan is stealing from customers of Android and iOS smartphones. The malware, often known as Spark Cat, was present in apps obtainable within the official Google and Apple app shops. After putting in the contaminated app, it requests entry to the picture storage.
This doesn’t normally arouse suspicion, as Spark Cat and its successor Spark Kitty cover in chat apps, for instance.
Sending images through chat apps is frequent and naturally requires entry to images.

This app was obtainable in Google’s official app retailer and was contaminated with the Spark Cat spyware and adware Trojan. The malware searches the smartphone’s picture storage for passwords, which it extracts utilizing OCR.
Foundry
Hazard: On Google Playalone, Kaspersky’s safety researchers counted 10 apps contaminated with Spark Kitty that had been downloaded over 240,000 instances. In Apple’s App Retailer, the malware was present in 11 contaminated apps.
The malware searches the cellphone’s picture storage for screenshots containing passwords or different secret data. The textual content is extracted utilizing OCR recognition after which utilized by the attackers to entry crypto wallets. This permits them to steal massive sums of cash from their victims’ accounts.
Safety: The tried-and-tested methodology of solely downloading apps from official app shops is sadly of no assist right here. In spite of everything, the malware was present in apps from these shops. In future, it’s best to due to this fact additionally take note of how usually an app has been downloaded. Apps with 1,000,000 or extra downloads are almost certainly secure.
Additionally, take note of the permissions an app requests. You must solely grant entry to your picture storage after cautious consideration. And as a common rule, delicate data equivalent to passwords shouldn’t be saved in screenshots. These belong in a password supervisor. See our article on the perfect password managers.
5. Assaults on printers
In June 2025, safety researchers at Speedy 7 found eight vulnerabilities in a whole lot of printers from varied producers.
Hazard: Attackers can use these vulnerabilities to realize entry to the community and knowledge. The businesses affected are Brother, Fujifilm, Ricoh, Toshiba, and Konica Minolta. Though the businesses have supplied firmware updates, the safety vulnerability can solely be closed with a workaround.
This vulnerability bypasses authentication, permitting attackers to realize management of the gadget. To log in, attackers use the gadget’s default password, which consists of its serial quantity. This may be retrieved through one other vulnerability.
Safety: Change your printer’s default password and set up the newest updates to your gadget.
6. Browser add-ons empty crypto wallets
Browser extensions containing malicious code are popping up many times. Most just lately, the criminals behind these extensions focused house owners of crypto wallets.
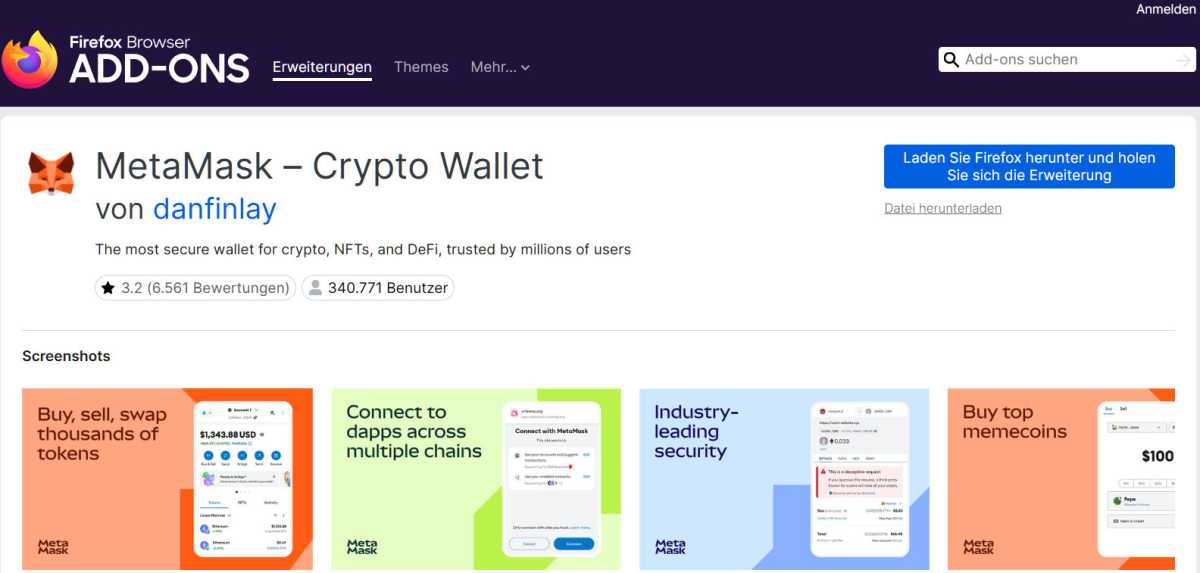
This can be a Firefox extension for the Meta Masks crypto trade. It’s usually troublesome to find out whether or not these extensions are innocent or not. Nonetheless, a excessive variety of downloads means that an add-on is innocent. Having a look on the developer’s web site additionally helps with the evaluation.
Foundry
Hazard: Dozens of pretend browser add-ons for Firefox are designed to steal entry knowledge for cryptocurrency wallets. The extensions fake to be legit pockets instruments from well-known platforms equivalent to Coinbase, Meta Masks, or Belief Pockets.
A few of the roughly 40 harmful add-ons are even stated to have made it into Firefox’s official add-on market, as reported by the discoverer Koi. To do that, the attackers used the open-source code of well-known add-ons and positioned their malicious code in them.
The add-on was then posted on-line beneath a reputation much like the unique.
Safety: Solely obtain browser extensions from trusted sources. Even then, be sure that the add-on has been downloaded many instances earlier than.
Since extensions can replace routinely, there’s additionally a danger that add-ons that had been initially innocent may very well be contaminated with malicious code after an replace. Due to this fact, uninstall any extensions that you just not want.
7. Deepfakes
Deepfakes are faux images, audio information, or movies. They will trigger quite a lot of injury, as a result of even cautious folks might be misled by the fakes.
One instance is a faux livestream of Nvidia’s keynote speech in October 2025: Concurrently the actual livestream on YouTube, fraudsters broadcast a deepfake video that includes an AI-generated Jensen Huang, CEO of Nvidia.
Nonetheless, he didn’t speak about new chips at Nvidia, however a couple of new cryptocurrency undertaking. The faux stream is alleged to have had extra viewers than the actual one at the start: 100,000 for the deepfake in comparison with 12,000 for Nvidia.
The rationale for this was in all probability that YouTube displayed the deepfake first within the outcomes listing when trying to find “Nvidia Keynote.” It took YouTube half an hour to take the faux offline.
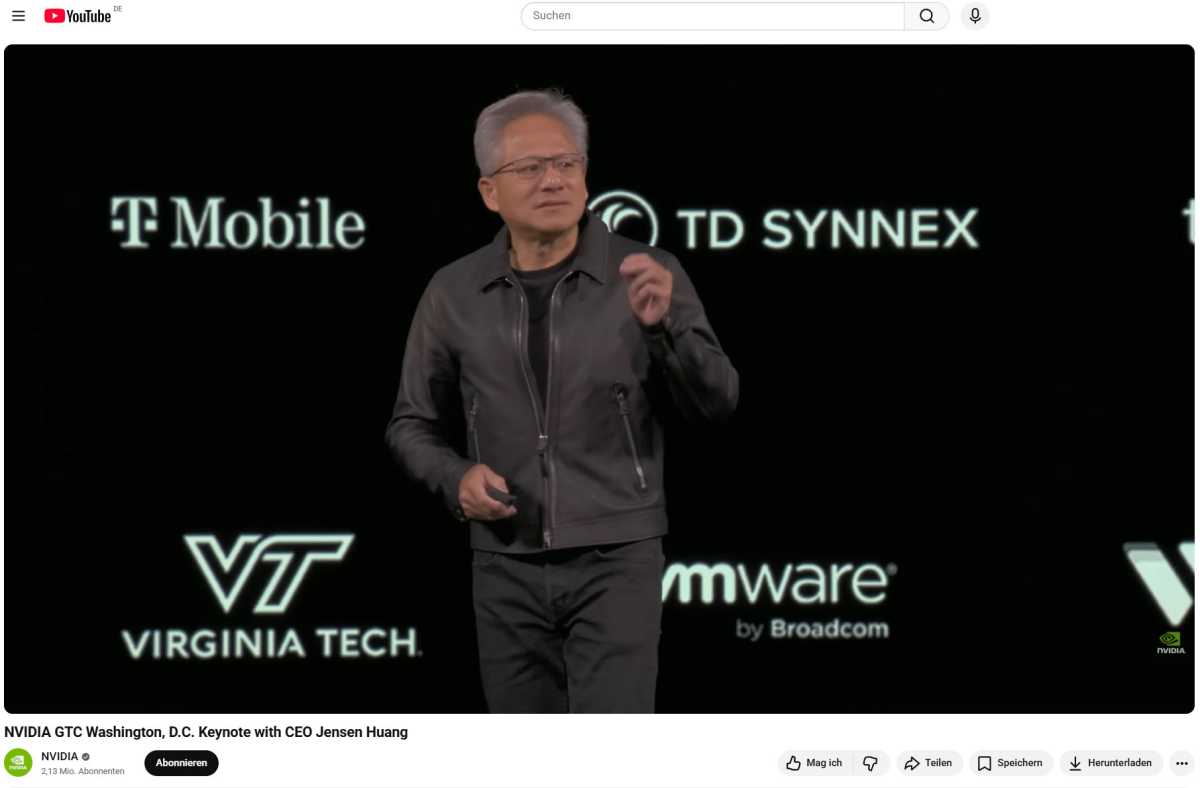
The actual Jensen Huang, CEO of Nvidia, at the actual keynote in October 2025. On the similar time, a deepfake of the keynote with Jensen Huang was operating on YouTube. In it, he marketed a cryptocurrency.
Foundry
Hazard: Criminals use cryptocurrencies to steal cash from unwary customers. These scams normally contain false guarantees of fast income with crypto cash which can be truly nugatory. Deepfakes are sometimes used for this objective.
Manipulation is then used to rapidly enhance the obvious worth of the cash, which prompts the victims to purchase. As soon as a sure worth is reached, the fraudsters promote their shares in a single fell swoop and make a revenue. The worth of the cryptocurrency falls quickly, so that everybody else normally suffers a whole loss.
Safety: You must solely put money into cryptocurrencies if you’re very conversant in the topic. Then the everyday crypto scams are simple to identify.
8. Ransomware with AI
Safety researchers at Eset have found malware referred to as Immediate Lock. It makes use of synthetic intelligence particularly for ransomware assaults.
Hazard: The blackmail virus makes use of a domestically put in language mannequin that independently generates scripts throughout the assault and thus decides for itself which information to go looking, copy, or encrypt.
A perform for the everlasting destruction of information is seemingly already built-in, however has not but been activated. Immediate Lock creates cross-platform Lua scripts that may run on Home windows, Linux, and Mac OS.
Safety: The finest safety in opposition to ransomware is an up-to-date knowledge backup that’s saved individually from the system. You could find extra suggestions in our information to ransomware.
9. Attackers crack doorways
Sensible units for house networks normally additionally supply web entry to their features. Whereas that is handy, it additionally carries dangers.
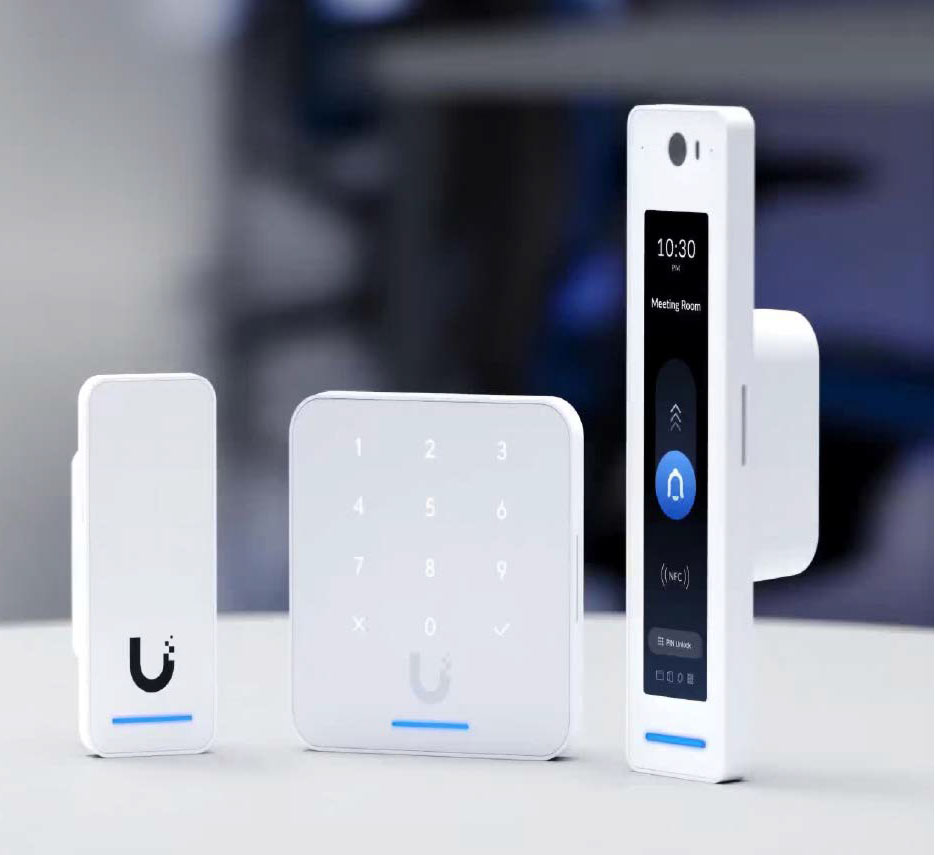

The administration software program for Unifi’s sensible door locks contained a safety vulnerability with the best vulnerability ranking (CVSS 10). Hackers may in all probability simply crack a door protected by Unifi.
Unifi
Hazard: Vulnerabilities in sensible units turn into threatening when an attacker can use them to penetrate the house community and steal knowledge. The next case can also be very disagreeable: A sensible doorbell has a vulnerability that attackers can use to open the lock.
This was apparently the case in October 2025 with door locks from the corporate Unifi. The Unifi Entry Software entry software program contained a safety vulnerability with a CVSS rating of 10, as introduced by the producer itself.
It didn’t reveal precisely what the vulnerability and the corresponding assault strategies appear like. Nonetheless, the CVSS rating of 10, which is the best doable ranking, means that the vulnerability might be simply exploited with huge penalties.
Safety: Model 3.4.31 of Unifi Entry Software, which is aimed toward companies, is affected by the vulnerability. Directors ought to replace to the newest model.
Normally, it’s best to recurrently verify for updates to the firmware and administration software program for all sensible house and community units. Vulnerabilities in these units can have critical penalties.
This text initially appeared on our sister publication PC-WELT and was translated and localized from German.




