The street to quantum datacentres goes past logical qubits
One of many questions everybody concerned in quantum computing is requested is, “When will the expertise change into commercially viable?”
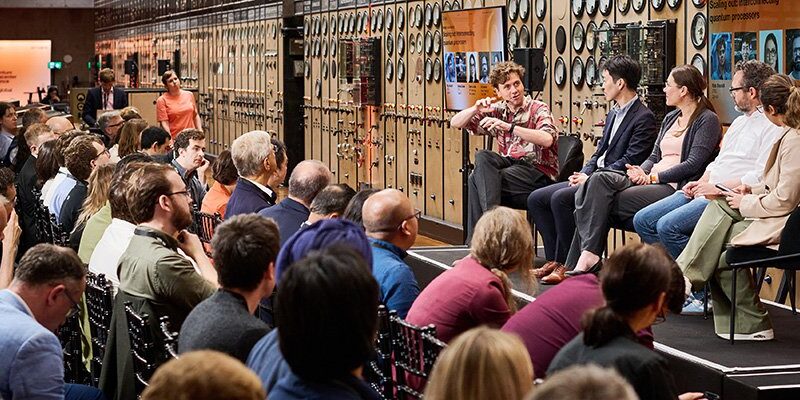
This very query was posed to a panel of consultants on the inaugural Quantum Datacenter Alliance Discussion board in London by Austin Li, who’s engaged on quantum computing requirements at Google and serves as chair and head of america Delegation to the IEC/ISO Joint Technical Committee on Quantum Applied sciences Requirements.
Though there tends to be a whole lot of business noise round logical qubits and error correction, that are wanted to make quantum computer systems which can be able to performing helpful duties, quite a few items of the jigsaw required for a totally working and scalable quantum computing system are lacking.
Esoteric {hardware}
Talking on the discussion board, Alexander Keesling, chief expertise officer at QuEra, mentioned the bounds of lasers, that are being optimised for fully completely different software areas. “You will discover very high-powered lasers, however these lasers don’t have any type of coherence,” he stated, which makes them unsuitable to be used in quantum computer systems.
One other problem the business must resolve, in line with Keesling, is scalability. Realistically, a system with twice the variety of qubits mustn’t require a machine that’s twice the scale, he stated, including that the infrastructure required by a quantum laptop should be stored in examine because the variety of qubits will increase.
“If we simply construct one other system subsequent to a quantum laptop after which determine learn how to join it, I might say that it’s extensible. It’s not scalable,” he stated.
Owen Arnold, vice-president of product growth at Oxford Quantum Circuits, mentioned the challenges in working with suppliers of dilution fridges, that are wanted to realize a superconductive surroundings, as required by some quantum laptop methods. “These are very spectacular, however they’ve largely been constructed for an instructional market,” he stated.
In Arnold’s expertise, the producers of dilution fridges want to think about how such specialised gear may be scaled to function in a datacentre surroundings. “In the event you want a dilution fridge, then you’ll need the experience to run that dilution fridge,” he added.
One other consideration is that quantum computer systems are typically constructed for experimentation. “The experiment goes down; it fails, which is essentially acceptable. A small variety of persons are affected by that,” he stated.
However when you think about the ambitions of the quantum computing business to deploy such machines in datacentres, it’s now not simply an experiment that may fail with restricted disruption. As a substitute, five-nines (99.999%) uptime is required. “We wish to have a lot better diagnostics for these items. We wish to management the upkeep cycle, and we wish to ensure that the redundant energy is there,” Arnold added.
Even when the science behind quantum computing can progress to the purpose the place it could actually carry out with a excessive diploma of reliability, and the business could make datacentre-ready quantum computing methods, ease of programmability will should be addressed to realize datacentre-scale adoption.
Ease of programming and hybrid complexity
Josh Savory, director of providing administration at Quantinuum, mentioned the corporate’s 2029 roadmap on the discussion board, and the challenges it might want to overcome to ship one thing commercially viable by then. He believes there must be business alignment round requirements.
Savory stated QIR, the community-wide effort to design and implement the mandatory compiler expertise to speed up advances in quantum programming language design, and CQASM, a programming language for quantum computing that gives a approach of expressing quantum circuits as code, are wanted to offer a uniform programming interface for software builders.
The panel of consultants additionally mentioned how quantum computer systems would match alongside classical high-performance computing (HPC) as a type of coprocessor. Whereas this method could possibly be the path of journey for a lot of quantum computing corporations in deploying their machines in datacentres, such an structure is vastly complicated.
“How the varieties of issues that we try to resolve as we speak may be accelerated with a quantum laptop continues to be unknown,” stated QuEra’s Keesling.
Components like contemplating the applying code that may be despatched to a quantum laptop with code that’s greatest run on HPC structure, and orchestrating between these completely different lessons of compute assets, are questions the business might want to reply if a hybrid method is adopted.
There was loads of analysis into quantum computing that means the objectives of the business are achievable, at the least from a expertise perspective. However the message from the panel of consultants on the Quantum Datacenter Alliance Discussion board was {that a} heck of much more work must be finished earlier than these machines can actually scale in a industrial datacentre setup.